Active Listening
Active Listening is a meditation-like skill that involves fully concentrating on what a person is saying the entire time they are talking.

What is Active Listening?
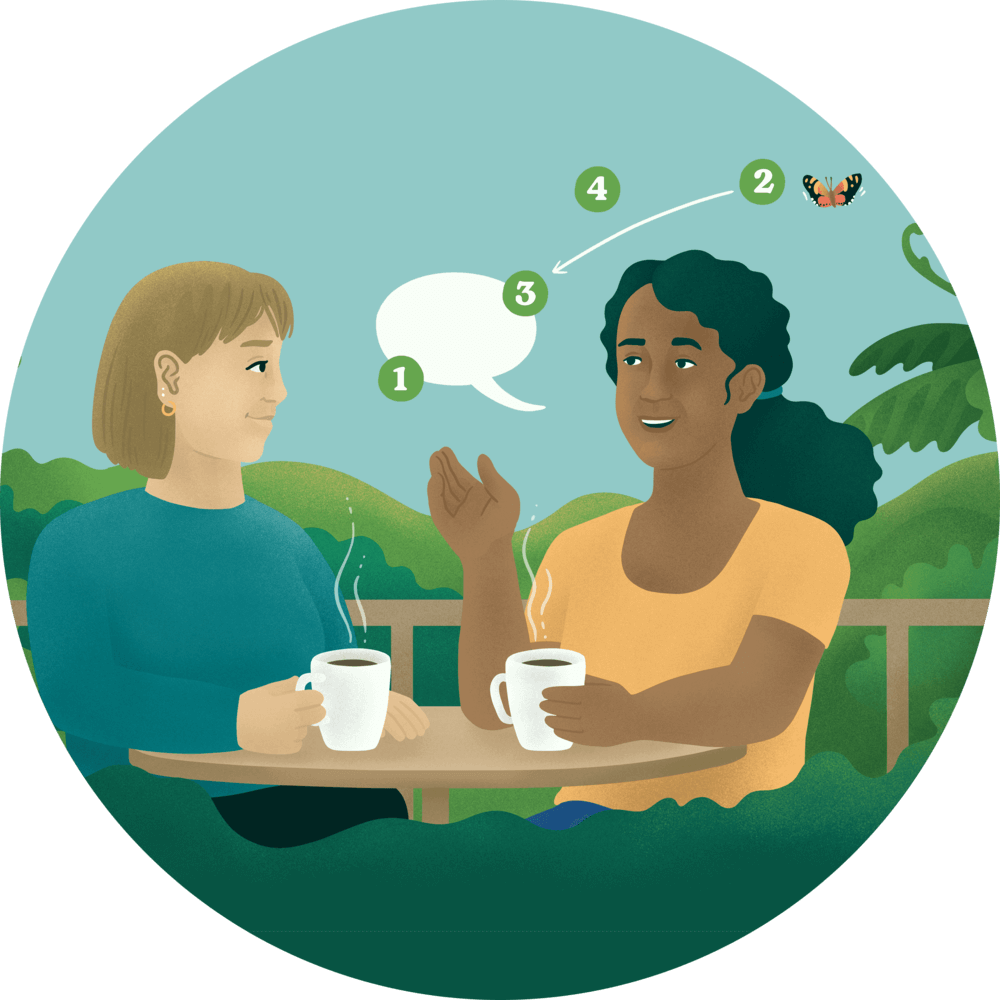
Active Listening is a skill that involves fully concentrating on what a person is saying the entire time they are talking,
During our Active Listening exercise, you will practise listening to people speak about their lived experiences and pick up moments when you’re not paying attention.
How does it help?
Noticing when your mind wanders and bringing your attention back to listening helps you to listen and hear others. Active listening can help you respond to people in ways that make them feel understood, prevents you from interrupting them unnecessarily, and can improve your relationships with friends, partners, whānau, co-workers and other people in your life.
FAQs
What is selective listening?
It’s normal to get caught up in our thoughts sometimes when people are talking. You might start forming opinions about what they’re saying or thinking about how you are going to respond. Selective listening is when we only listen to some of what is being said and, as a result, can miss key details.
How can I further develop my listening skills?
The key is to apply active listening techniques in your everyday interactions. You won’t have a button to push when you become distracted by your mind, but you can say “I’m not listening” to yourself. Then, let that thought go and calmly refocus on what the person is saying.
It may be helpful to summarise what they’ve said back to them, which shows that you were listening and gives them the opportunity to point out anything you’ve misheard or misunderstood.
What are some examples of Active Listening skills?
- Facing the speaker and maintaining an appropriate level of eye contact.
- Remaining neutral and non-judgmental in response to what they say.
- Being patient (periods of silence are not "filled") - resisting interrupting and trying to impose ‘solutions’ or finish sentences for the speaker.
- Using verbal and non-verbal feedback to show signs of listening. For example, smiling, eye contact, leaning in, mirroring body language.
- Asking questions and listening to the answer attentively.

Try Active Listening now
Small Steps Toolbox
These tools have been developed to help with feelings of anxiety, stress, or low mood. Each tool only takes a few minutes. Health and wellbeing is an ongoing journey - so try them out and see what works for you.
Te Whakatau i te Wairua
Mā tēnei tūmahi ka kite koe i te pānga o ō mahi ki ō kare ā-roto. Kei konei hoki ētahi tūmahi hei hiki ake i ō kare ā-roto.
Te Mātai Aronui
I tēnei tūmahi mātai aronui, ka arahina koe e tētahi oro māmā ki te āta rapu atu i ngā āhuatanga rerekē o ētahi whakaahua, ā, kia pērā anō tō titiro ki tō ao.
Te Whakahou i ngā Whakaaro
Mā tēnei tūmahi, hei tautohu ngā tauira hua-kore e whāia ana e ō whakaaro me ō whakapono, ā, ki te whakahoungia ērā āhuatanga, i roto i te wā, ka pai ake ai ō kare ā-roto, ka pai ai hoki ō whakatau hei hiki anō i tō hauora.
Te Mōhio ki ngā Tohu
I tēnei tūmahi, ka arahina koe ki te tautohu i ngā rongo o te tinana i te wā e pā kinohia ana tō ngākau. Mā ēnei tohu koe hei ārahi ki tētahi ara rerekē, arā, ki te mahi i tētahi o ngā tūmahi, ki te te tiaki rānei i a koe anō.
Te Āta Whakahā
He tikanga whakaataata tēnei, e āta whakahā ai te tangata, ki roto, ki waho anō kia tau te mauri, kia whakatā hoki te wairua. E arahina ana tēnei tūmahi e tētahi ata tāoreore e ngongo ana, e tuku ana hoki i te hau.
